What is Subspine Impingement (SSI)?
Subspine impingement, also known as anterior inferior iliac spine impingement, is a hip condition characterized by excessive friction caused by bony irregularities on the extraarticular (outside of the joint) surfaces of the hip bones rubbing against each other.
Causes of Subspine Impingement
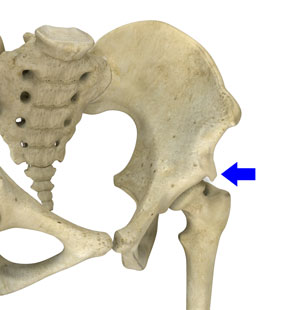
Subspine impingement occurs when the anterior inferior iliac spine, which is a prominent bony process on the ilium of the hip bone impinges on the neck of the thigh bone (femur) during hip flexion.
Types of Subspine Impingement
Subspine impingement is classified based on the location and shape of the anterior inferior iliac spine on the ilium of the hip:
- Type1: In this case, there is a normal anterior inferior iliac spine which does not extend to the hip socket rim and as a result, there is no active hip impingement.
- Type 2: There is an enlarged anterior inferior iliac spine that extends near the rim of the socket which can result in hip impingement and pain.
- Type 3: The anterior inferior iliac spine is low lying and extends below the rim of the hip socket. This impingement causes a restriction in hip flexion and internal hip rotation.
Symptoms of Subspine Impingement
Symptoms of Subspine impingement include:
- Restricted hip movement
- Bruising in the labrum
- Deposit of calcium in the rectus muscle
- Pain in the buttocks or outer thigh area
- Difficulty in walking uphill
- Inflammation in the synovial membrane
- Hip pain
Diagnosis of Subspine Impingement
Your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms and based on the information, a physical examination will be performed. Certain diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans may be ordered to detect bone deformity. Your doctor will conduct an impingement test during which you will be asked to move your knee towards your chest and rotate it towards your opposite shoulder. This aids in the diagnosis of hip pain.
Treatment for Subspine Impingement
Treatment for subspine impingement is based on the severity of impingement and the occurrence of deformity. Some of the common treatment methods include:
Conservative Method
- Rest
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- Injection of steroids and analgesics into the hip joint
If conservative methods fail to improve the symptoms, surgery will be recommended:
Subspine Decompression: This is a minimally invasive technique performed arthroscopically in which small incisions are made through which an arthroscope, a thin flexible tube with a camera at one end, is inserted into the hip joint to view the joint surface. Small surgical instruments are then inserted through the other portals to perform the decompression. Subspine decompression may include the following procedures:
- Debridement: This removes loose bodies from the hip joint.
- Shaving: This tool is used to smooth bony protrusions.
- Avulsion fracture removal: The bone fragment that has become detached from the subspine area, as well as the muscle and tendon, will be removed using this technique.
- Femoroplasty: A femoroplasty is a surgical procedure to reshape the femoral bone.


